It’s a last quarter of 2018 and we can see how extensively leading network equipment vendors, solution providers and communication service providers (CSPs) are moving towards next generation of connectivity network in the form of 5G. This shift leads to growing maturity and development in network functions virtualisation (NFV) technology driven by active contribution by open source communities as well as work around new innovative proof of concepts jointly implemented by commercial vendors, writes Sagar Nangare, a digital strategist at Calsoft.
In this article, we’ll explore how DevOps methodology is implemented by vendors like Intel, Netrounds, Rift.io, Arctos labs with the help of ETSI’s Open Source MANO (OSM).
The need for service assurance
On a roadmap of a scenario where multiple virtual network functions (VNFs) are chained together to create a network service and testing implementation of 5G feature such as network slicing wherein network channels are getting sliced to support different use cases to be enabled with 5G, service providerscare about ensuring and maintaining consistent quality of service to end users. After all, transformation to 5G is so CSPs can provide a good customer experience.
However, transforming to 5G brings great complexity in network architecture and operations plus inclusion of shared environments; like for example VNFs deployed in virtual machines (VMs) may need an update to enhance feature of service or it may be an immediate patch to avoid a glitch. Probably, such changes can be much frequent due to enablement of software nature in place of network equipments. To address the update, it will be difficult for service providers to perform manual testing and validation which may halt service delivery to active end customers. Service providers should ensure stability in service provision by active monitoring and testing at each phase network service. And, in case of network slicing feature, it becomes prominently critical for service provider where customer demand is aligning to use cases having low latency. Each of network slice has defined critical service level agreements (SLAs) requirements to meet.
So, summarising the above, service providers need to
- Validate critical SLAs (matching customers and use cases) required by each of the network slices by actively monitoring and measuring metrics received at slices.
- Find out issues and resolve it in run time without affecting the service delivery.
There is a gap between how you monitor/test network services and ensure the quality of services to customer and tools and solutions.
PoC implementation to address challenge
To address the above challenges, it becomes imperative for service providers to have an active testing and validation that is highly automated by using programmable APIs in service chains and, end to end monitoring of services.
The proof of concept (PoC) implemented by Telenor, Intel, Arctos Labs, Netrounds, Rift.io, and ETSI OSM addresses the above monitoring and service assurance concerns.
The PoC utilised MANO for automated network service lifecycle management and end-to-end service activation, validation, and operations. DevOps approach is used for network operations and network service design plus enabling automation of deployment and maintenance of service chains and 5G slices.
The key feature of this demonstration is testing of new services is added at design time of network service or service chains. Adding to it, delivery or updates to new network services is verified during run time; if in case any update fails to execute, it can be roll back before reaching to customers.
PoC architecture and example
As a sample case for this PoC a network slicing scenario containing three different slices are considered which are having different type of characteristics, output for customers and key performance indicators (KPIs) to meet requirements from services that service providers are delivering. Here in this examples, slices involved are: Mobile broadband having an important KPI as throughput, Massive IoT targeted KPI is packet loss and for industrial automation targeted KPI is latency.
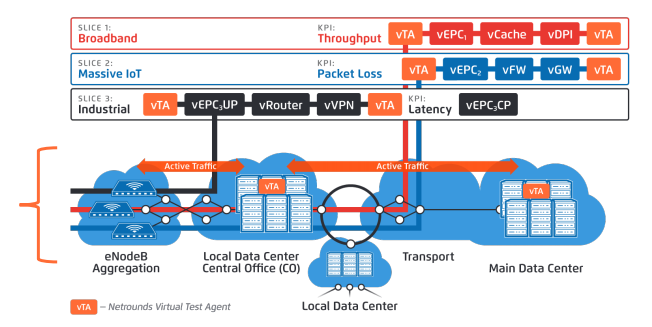 Fig – PoC Example
Fig – PoC Example
ETSI Open Source MANO is used in conjunction with RIFT.IO’s RIFT.ware solution for NFV orchestration while OpenStack was used as the virtual infrastructure manager (VIM).
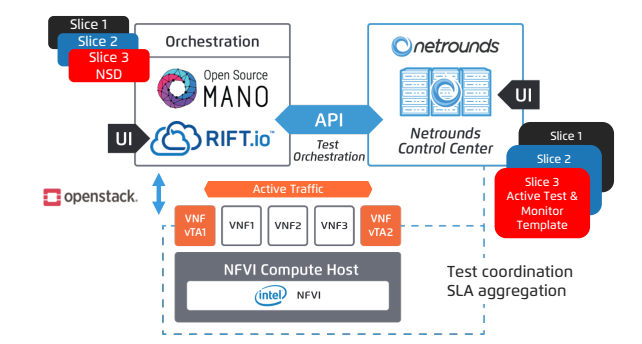 Fig – PoC demo architecture
Fig – PoC demo architecture
In order to test and assure the expected quality of service levels by network services and to be able to measure the KPIs of network slices, the Netround’s vTAs (virtual test agents) are deployed as part of the service. These test agents used for actively generate traffic, analyse details and for real time measurements across service applications and interfaces. vTAs are controlled and updated remotely through Netrounds’ unifying Control Center hosted by at Netwounds end or on premises. Here is how the sample network service will look alike
For a large scale implementation of 5G network slices comprise of different but targeted service chains, an active end to end service assurance can be achieved with real time monitoring and testing empowered with DevOps for automating operations. The key part of this PoC is the deployment of virtual test agents as part of network service chains to keep an eye during lifetime of service. It can send real time insight to control center about the health of the service.
You can get more details about this PoC from this whitepaper published on ETSI OSM website and watch a live demonstration here.






